Industrial
Automation
& Controls

Contact Info | Reference | Email Login | Samples | Site Map
A Color Study is an analysis of the proposed color combinations for an HMI to determine the usability of those colors.
The most important thing to remember is that:
The subject of color perception is very complex and is far outside the scope this web site. Very briefly, the human eye has two types of light sensitive cells: rods and cones. The rods are most useful during low light condition: they are optimized for luminosity rather than color perception, and are better at detecting motion. The cones, however, are optimized for normal daylight. There are 3 types of cones: each sensitive to a different wavelength of light (short, medium, and long). Sometimes these are referred to as blue, green and red receptors, but that is misleading because each cone is:
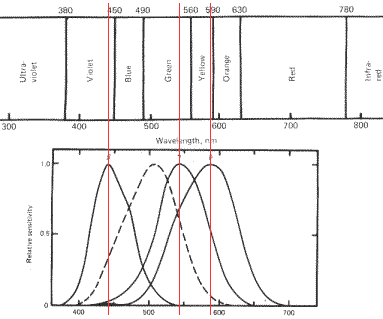
In some people, one or more of these cone types has a reduced sensitivity to light (or may be missing altogether), which causes these people to perceive colors differently from people with normal cones. Roughly 8% of men and 0.4% of women have some sort of color deficiency.
The most common types of color deficiency are:
It is very common to see colors used in an HMI to convey information: A motor might appear:
A valve might appear:
A light panel might appear:
Or text might change color based on any of these conditions.
The following screenshots show some typical HMI conventions and how they might appear to people with different color deficiencies. Pay particular attention to how colors are used to indicate the following:
Note that certain combinations may work with some types of color deficiency but not with others.
This section shows 10 screenshots from an application that has been optimized for people with Deuteranopia, Deuteranamoly, Protanopia, and Protanamoly. (It has not been optimized for Tritanopia, which is very rare.) Each of the 10 examples also shows what that screen might look like to people with different color deficiencies. We have adopted the following conventions to make sure all operators can distinguish the alternative colors. And, of course, we never rely entirely on color to convey meaning.
Chiller 1A
Chiller 1C
Oil Separation 1C
Oil Storage 1A
Oil Storage 1C
Sales Gas 1A
Sales Gas 1C
Vapor Recovery Compressor 1C
Variable Speed Drives 1